In today’s increasingly eco-conscious world, understanding the environmental impact of our actions is paramount. This is where the Life Cycle Inventory (LCI) comes into play. A comprehensive analysis of the energy and material inputs, outputs, and environmental impacts associated with a product’s life cycle, LCI helps us unlock valuable insights into sustainable practices. From the extraction of raw materials to production, use, and disposal, LCI enables us to assess the environmental hotspots and identify areas for improvement.
With LCI, businesses and individuals alike can make informed decisions, reduce their carbon footprint, and contribute to a greener future. By quantifying the resources consumed, emissions generated, and waste produced at each stage of a product’s life cycle, LCI provides a holistic perspective on environmental impact. It enables us to identify opportunities for more sustainable materials, processes, and practices, ultimately leading to more conscious consumption and production.
In this article, we dive deep into the world of Life Cycle Inventory, exploring its significance, methodology, and applications. Join us as we unravel the power of LCI in unlocking insights into environmental impact and sustainable practices.
Importance of Life Cycle Inventory in Understanding Environmental Impact
The importance of the Life Cycle Inventory in understanding environmental impact cannot be overstated. By quantifying the resources consumed, emissions generated, and waste produced at each stage of a product’s life cycle, LCI provides a holistic perspective on environmental impact. This allows businesses and individuals to make informed decisions, reduce their carbon footprint, and contribute to a greener future.
LCI helps us identify the environmental hotspots in a product’s life cycle, highlighting areas with the highest impact. For example, it may reveal that the production phase contributes significantly to greenhouse gas emissions, or that the disposal phase generates large amounts of waste. Armed with this information, businesses can focus their efforts on improving these specific areas and implementing more sustainable materials, processes, and practices.
What is the Life Cycle Inventory (LCI)?
Life Cycle Inventory (LCI) is a systematic approach to quantify the energy and material inputs, outputs, and environmental impacts associated with the entire life cycle of a product. It involves gathering data on the various stages of a product’s life, including raw material extraction, manufacturing, distribution, use, and disposal. This data is then analyzed to assess the environmental burdens and resource consumption associated with each stage.
The goal of LCI is to provide a comprehensive understanding of a product’s environmental footprint, allowing for informed decision-making and the identification of opportunities for improvement. By taking into account the entire life cycle, LCI goes beyond traditional environmental assessments that focus solely on specific stages or processes.
Key Components of a Life Cycle Inventory
A Life-Cycle Inventory typically consists of four key components: goal and scope definition, inventory analysis, impact assessment, and interpretation. These components work together to provide a comprehensive understanding of the environmental impact of a product throughout its life cycle.
1. Goal and Scope Definition:
This component involves clearly defining the goals and boundaries of the LCI study. It includes determining the purpose of the study, the system boundaries (i.e., which stages of the life cycle will be included), and the functional unit (e.g., the amount of product or service being analyzed).
2. Inventory Analysis:
The inventory analysis involves collecting data on the energy and material inputs, outputs, and environmental emissions associated with each stage of the product’s life cycle. This data is typically collected from a variety of sources, including industry databases, government reports, and primary research.
3. Impact Assessment:
The impact assessment component involves evaluating the potential environmental impacts of the inventory data collected. This may include assessing factors such as greenhouse gas emissions, water usage, land use, and toxic releases. Various impact assessment methods and indicators can be used to quantify and compare the environmental impacts across different stages of the life cycle.
4. Interpretation:
The interpretation component involves analyzing the results of the inventory and impact assessment to draw meaningful conclusions. This includes identifying the environmental hotspots, evaluating the significance of the impacts, and identifying opportunities for improvement. The results of the interpretation can then be used to inform decision-making and guide the development of more sustainable practices.
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) and its Relationship to Life Cycle Inventory
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) is a broader concept that encompasses Life Cycle Inventory (LCI) as one of its components. While LCI focuses on the data collection and analysis of a product’s life cycle, LCA takes a more comprehensive approach by considering the potential environmental impacts of a product or service throughout its entire life cycle.
LCA includes additional components, such as impact assessment and interpretation, to provide a holistic view of the environmental performance of a product or service. By considering the entire life cycle, LCA enables a more accurate assessment of the environmental impacts and allows for more informed decision-making.
LCI, on the other hand, specifically focuses on the inventory analysis component of LCA. It provides the foundational data needed to quantify the energy and material flows, as well as the environmental emissions and impacts associated with a product’s life cycle. LCI is an essential tool within the broader framework of LCA, providing valuable insights into the environmental hotspots and opportunities for improvement.
Benefits of Conducting a Life Cycle Inventory Analysis
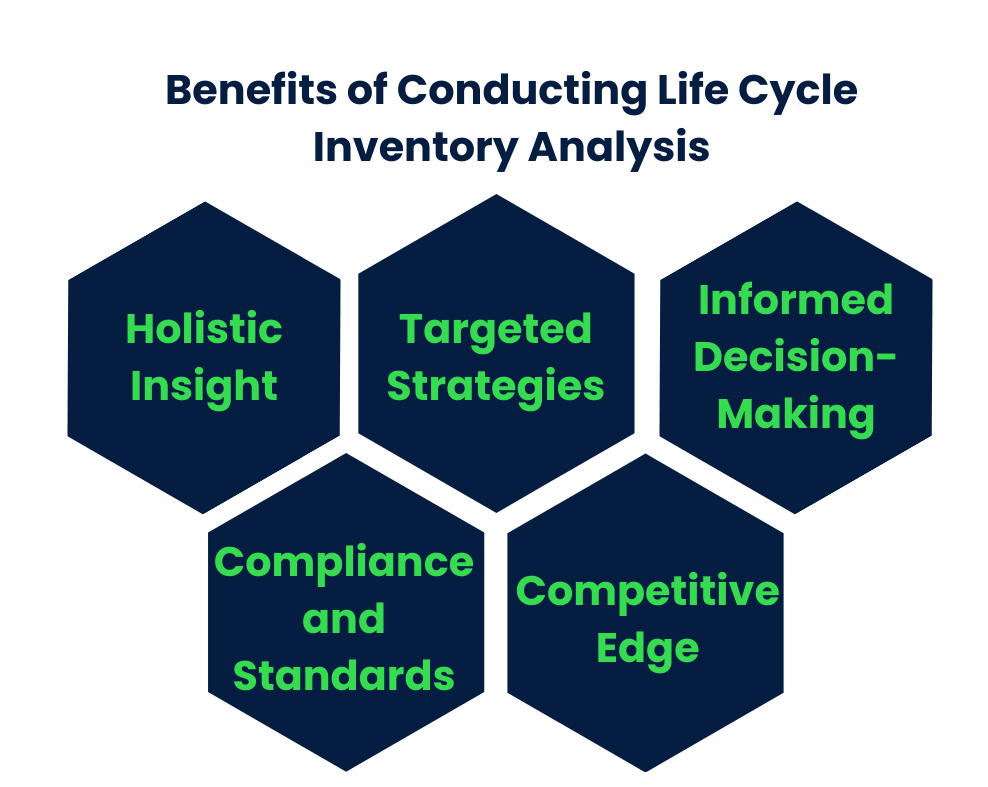
Conducting a Life Cycle Inventory (LCI) analysis offers myriad benefits for businesses and individuals aiming to reduce their environmental impact and embrace sustainability.
- Holistic Insight: LCI provides a comprehensive understanding of a product’s life cycle, facilitating pinpointing areas of highest environmental impact.
- Targeted Strategies: Armed with LCI insights, companies can focus efforts on reducing resource consumption, emissions, and waste generation, thus optimizing sustainability endeavors.
- Informed Decision-Making: LCI enables informed decisions in product development and material selection, aligning choices with sustainability goals, leading to cost savings and improved brand reputation.
- Compliance and Standards: LCI aids benchmarking against industry norms and regulations, ensuring proactive adherence and continuous environmental improvement.
- Competitive Edge: Integrating LCI practices enhances competitiveness by appealing to eco-conscious consumers, attracting investors, and fostering brand loyalty.
In summary, LCI analysis empowers businesses to understand their environmental footprint, make informed decisions, drive targeted sustainability initiatives, ensure compliance, and gain a competitive advantage.
Challenges and Limitations of Life Cycle Inventory Analysis
While Life Cycle Inventory (LCI) analysis offers invaluable insights into environmental impact and sustainable practices, it is not without its challenges and limitations.
Data Availability and Quality:
A significant hurdle in LCI is the availability and quality of data. Collecting precise and dependable data for each stage of a product’s life cycle can be time-consuming and expensive. Data gaps and inconsistencies may arise, undermining the accuracy of the analysis and complicating the derivation of meaningful conclusions.
Complexity:
LCI analysis is inherently complex due to the interconnectedness of different life cycle stages and the multitude of variables involved. This complexity can pose difficulties in accurately assessing the true environmental impact of a product. Assumptions and simplifications may be necessary, introducing uncertainties into the analysis and potentially skewing results.
Limited Scope:
LCI analysis predominantly focuses on environmental factors and often overlooks social and economic considerations. While it provides a comprehensive understanding of environmental impact, it neglects crucial aspects such as social equity and economic viability. To address this limitation, complementary tools like Social Life Cycle Assessment (SLCA) and Life Cycle Costing (LCC) can be employed alongside LCI to provide a more holistic perspective.
In essence, LCI analysis is potent for assessing environmental impact and sustainability. Challenges include data availability, complexity, and limited scope. Overcoming them demands careful consideration and supplementing with complementary frameworks. This ensures a more comprehensive product life cycle assessment.
Tools and Software for Conducting Life Cycle Inventory Assessments
To facilitate the process of conducting Life Cycle Inventory (LCI) assessments, various tools and software are available to businesses and individuals. These tools provide a streamlined approach to data collection, analysis, and interpretation, making LCI more accessible and efficient.
One widely used tool is the Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) software, which allows users to input data on the various stages of a product’s life cycle and automatically calculates the environmental impacts. LCA software often includes databases with pre-populated data, making it easier to gather information and perform the analysis.
Other tools and software focus specifically on the inventory analysis component of LCI. These tools provide templates and frameworks for data collection, as well as guidance on best practices and industry standards. They help streamline the data collection process and ensure consistency and accuracy in the analysis.
These tools simplify the LCI process but still need expertise. Understanding the methodology and limitations is crucial. You must also consider the specific LCI analysis requirements.
Watch Inventory Optimization Tool in Excel – Inventory optimization model on our SCMDOJO YouTube Channel!
Integrating Life Cycle Inventory into Sustainable Practices and Decision-Making
The insights gained from Life Cycle Inventory (LCI) analysis can be instrumental in integrating sustainable practices into business operations and decision-making.
By identifying the environmental hotspots and areas for improvement, LCI analysis helps businesses prioritize their sustainability efforts. This can involve implementing more sustainable materials, optimizing production processes, reducing energy consumption, and improving waste management practices. Companies can make significant progress by focusing on these areas. These areas include reducing environmental impact and adopting more sustainable practices.
LCI analysis helps businesses make informed decisions for product development and design. It considers the environmental impact of materials and processes. Companies can choose sustainable alternatives, that align with their goals. This leads to greener products, better resource efficiency, and less waste.
Furthermore, LCI analysis informs supply chain strategies. It assesses environmental impact. Companies make sustainable choices. They reduce their carbon footprint. Companies can source materials locally. They optimize transportation routes. They work with environmentally sustainable suppliers.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the Life Cycle Inventory (LCI) is a powerful tool for understanding product environmental impact and promoting sustainable practices. It quantifies resources consumed, emissions generated, and waste produced at each product stage. Moreover, LCI offers a holistic view of environmental impact, aiding informed decisions, carbon footprint reduction, and fostering a greener future.
While LCI analysis comes with challenges and limitations, the benefits outweigh the drawbacks. LCI analysis helps businesses identify the environmental hotspots, prioritize sustainability efforts, and optimize resource consumption. It also guides decision-making when it comes to product development, supply chain management, and material selection.
By harnessing the power of the Life Cycle Inventory, we can pave the way for a more sustainable future. Furthermore, it allows us to move towards more conscious consumption and production. This will ultimately reduce our environmental impact and preserve our planet for future generations. Let us embrace LCI as a valuable tool in our journey towards sustainability.